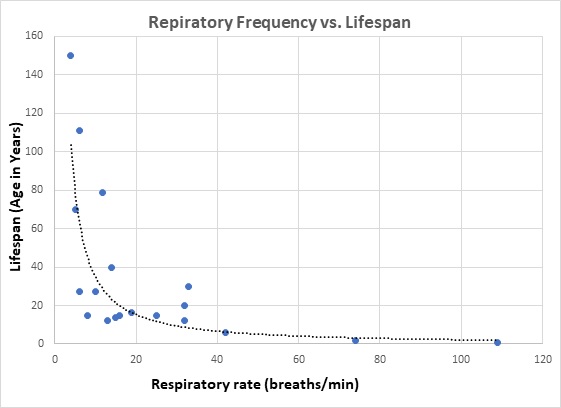
This is a scatter plot showing the relationship between breath frequency per minute and the lifespan of different animals including humans. At the extremes, the trend line shows that with the lowest breath frequency of 4 breaths per minute, the longest lifespan of 150 years is present. The trend line also shows that with the highest breath frequency of 109, the shortest lifespan of 1 year is present.
|
Species |
Respiratory Rate (br/min) |
Lifespan (Age in Years) |
|
Giant Tortoise |
4 |
150 |
|
Elephant |
5 |
70 |
|
Whale |
6 |
111 |
|
Bradypus Griseus (Sloth) |
6.2 |
27.5 |
|
Marmota Marmota (Rodent) |
8 |
15 |
|
Equus Caballus |
10 |
27.5 |
|
Adult Homosapien (Human) |
11.7 |
79 |
|
Choloepus hoffmanni (hoffman’s two-toed sloth) |
13 |
12 |
|
Chimpanzee |
14 |
40 |
|
Felis catus (domestic cat) |
15 |
14 |
|
Castor canadensis (American Beaver) |
16 |
15 |
|
Capra Hircus (Goat) |
19 |
16.5 |
|
Dogs |
25 |
15 |
|
Hereford Heifer (cow) |
32 |
20 |
|
Giraffa Camelopardalis |
32 |
12 |
|
Macaca mulatta (Rhesus monkey) |
33 |
30 |
|
Cavia porcellus (guinea pig) |
42 |
6 |
|
Mesocricetus auratus (Golden Hamster) |
74 |
1.75 |
|
Mus musculus (house mouse) |
109 |
1 |
References:
Altman, P. L. and D. S. Dittmer (1971) Respiration and Circulation. Bethesda, Md., Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Sarich, C. (2015, August 04). Living Like the Tortoise: Doubling Your Life Span with One Simple Breathing Technique. Retrieved July 18, 2018, from https://themindunleashed.com/2015/07/living-like-the-tortoise-doubling-your-life-span-with-one-simple-breathing-technique.html