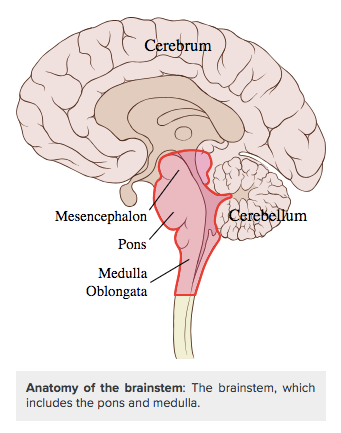
The pons and the medulla are the most used parts of the brain in the regulation of respiration. Involuntary respiration that is not under conscious control is controlled by centers of the upper brainstem. These centers are controlled by chemoreceptors that detect pH in the blood stream and can then change blood pH by increasing or decreasing the removal of carbon dioxide in the blood.
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/respiration-control/
The medulla oblongata is the main respiratory control center. It sends signals to the respiratory muscles to cause breathing to happen. The ventral respiratory group controls expiration while the dorsal respiratory group controls inspiration. The pons controls the rate and speed of involuntary breathing. There are two centers that achieve this task. The apneustic center signals for long and deep breaths and increases tidal volume. The pneumotaxic center inhibits breathing and can finely control the rate. Its signals inhibit the signals of the apneustic center and decreases tidal volume.
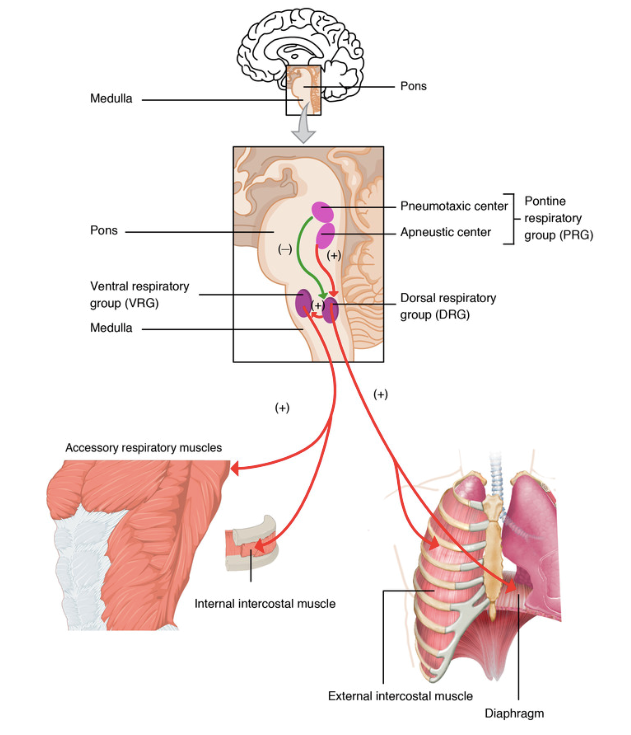
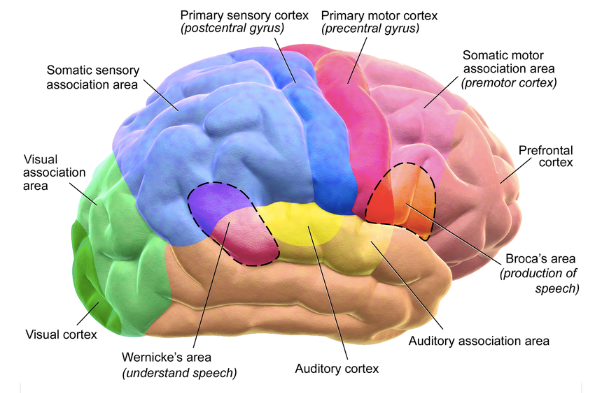
Voluntary respiration is controlled by the upper brain, specifically the cerebral cortex. In general, the motor cortex is what initiates any voluntary muscular movement. Respiration is controlled through activation of the diaphragm and accessory respiratory muscles. Different parts of the cerebral cortex are responsible for controlling different types of voluntary respiration. Contraction and relaxation of the internal and external intercostal muscles takes place in the superior portion of the primary motor cortex. Diaphragm control starts in a location posterior to the thoracic control. It is also believed that the inferior part of the primary motor cortex can be involved in controlled exhalation. Studies have also shown activity in the supplementary motor area and the premotor cortex during voluntary respiration. This could be associated with focus needed to voluntarily move muscles during breathing. Voluntary respiration can be easily overridden by signals from involuntary respiration, especially in times of danger.
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-ap/chapter/respiration-control/